What Makes a Fiduciary Financial Advisor Different from a Broker? sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with a casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
In this detailed exploration, we will delve into the distinct roles, legal standards, compensation structures, and client relationships that differentiate fiduciary financial advisors from brokers.
Overview of Fiduciary Financial Advisor vs. Broker
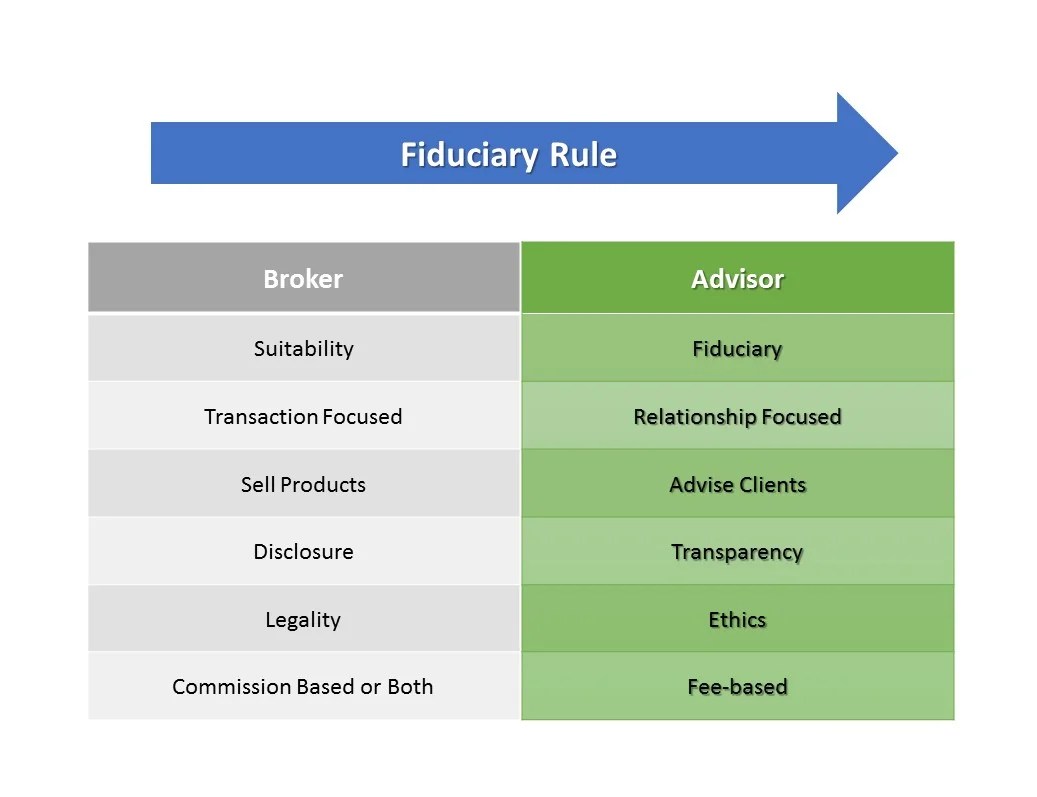
In the financial industry, fiduciary financial advisors and brokers play distinct roles in managing clients' assets and investments. Understanding the differences between these two professionals is crucial for investors seeking financial guidance.Fiduciary Financial Advisor:A fiduciary financial advisor is legally obligated to act in the best interests of their clients.
This means they must prioritize the client's needs above their own and disclose any conflicts of interest that may arise. Fiduciaries are held to a higher standard of care and must provide advice that is solely in the client's best interest.Broker:Brokers, on the other hand, are not held to the same fiduciary standard.
They are typically employed by brokerage firms and are focused on executing trades on behalf of clients to generate commissions. Brokers must recommend investments that are suitable for clients based on their financial situation, but they are not required to prioritize the client's best interests above all else.
Responsibilities and Obligations
- Fiduciary Financial Advisor:
- Act in the client's best interest at all times.
- Disclose any conflicts of interest.
- Provide comprehensive financial planning and investment advice.
- Broker:
- Recommend suitable investments for clients.
- Execute trades and transactions on behalf of clients.
- May receive commissions for selling specific products.
Key Differences
Fiduciary financial advisors prioritize the client's best interests, while brokers may have conflicts of interest due to commission-based compensation.
- Fiduciary Financial Advisor:
- Required to act in the client's best interest.
- Fee-based compensation structure.
- Focus on holistic financial planning.
- Broker:
- May have conflicts of interest.
- Commission-based compensation model.
- Primarily focused on executing trades.
Legal Standards and Regulations
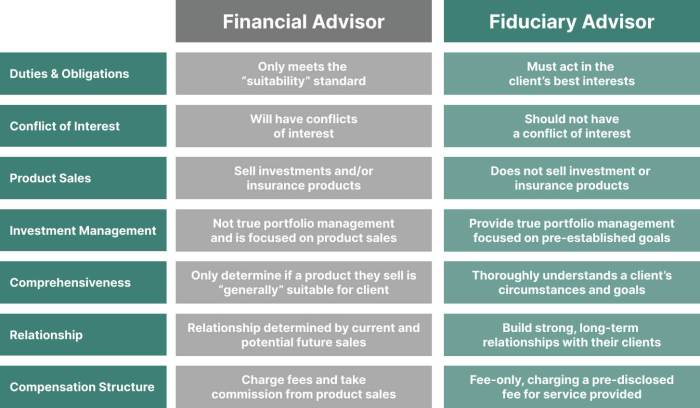
Fiduciary financial advisors and brokers are subject to different legal standards and regulations that govern their interactions with clients and the handling of investments. Understanding these requirements is crucial for investors seeking financial advice.
Legal Standards for Fiduciary Financial Advisors
Fiduciary financial advisors are held to a fiduciary duty, which means they are legally obligated to act in the best interests of their clients at all times. This duty requires them to provide advice that is solely aimed at benefiting the client, even if it means recommending strategies that may not be the most profitable for the advisor.
- Fiduciary advisors must disclose any potential conflicts of interest and prioritize the client's needs over their own.
- They are required to provide full transparency regarding fees, compensation, and any other financial incentives that could influence their recommendations.
- Any investment advice given must align with the client's financial goals and risk tolerance, putting the client's interests first.
Regulatory Requirements for Brokers
Brokers, on the other hand, operate under a suitability standard when recommending investments to clients. This standard requires brokers to recommend investments that are suitable for a client's financial situation and objectives, but it does not mandate that they act in the client's best interest at all times.
- Brokers must ensure that their investment recommendations align with a client's financial goals and risk tolerance, but they are not required to prioritize the client's interests over their own.
- They must disclose potential conflicts of interest, but the suitability standard does not demand the same level of transparency as the fiduciary duty.
- Brokers may receive commissions or other forms of compensation that could influence their recommendations, as long as the investments are deemed suitable for the client.
Compensation Structures
In the realm of financial advisory services, the compensation structures for fiduciary financial advisors and brokers play a crucial role in understanding their motivations and incentives when providing recommendations to clients.Fiduciary Financial Advisors:
Fee-based Model for Fiduciaries
Fiduciary financial advisors typically operate on a fee-based model, where they charge clients a set fee for their services, often based on a percentage of the assets under management. This fee is transparent and agreed upon upfront, ensuring that the advisor's compensation is directly tied to the client's financial success.
By aligning their interests with those of their clients, fiduciary advisors aim to provide unbiased and objective advice that prioritizes the client's best interests.Brokers:
Commission-based Model for Brokers
On the other hand, brokers commonly operate on a commission-based model, where they earn a commission for each financial product they sell to clients. This can create a conflict of interest, as brokers may be incentivized to recommend products that generate higher commissions for themselves, rather than those that are truly in the best interest of the client.
This compensation structure can lead to potential conflicts and raise questions about the objectivity of the advice provided.Overall Impact:The differing compensation structures between fiduciary financial advisors and brokers can significantly impact the advice and recommendations provided to clients. Fiduciary advisors, who operate on a fee-based model, are motivated to act in the client's best interest since their compensation is directly tied to the client's financial well-being.
In contrast, brokers, who earn commissions on product sales, may face conflicts of interest that can influence the recommendations they make. Clients should be aware of these compensation structures when seeking financial advice to ensure they are receiving unbiased and objective guidance tailored to their individual needs.
Client Relationships and Service Approach
When it comes to client relationships and service approach, fiduciary financial advisors and brokers have distinct ways of interacting with their clients. Fiduciaries typically prioritize personalized, holistic financial planning tailored to the individual needs and goals of each client. On the other hand, brokers often focus on executing transactions and may not always consider the broader financial picture of their clients.
Fiduciary Financial Advisors
Fiduciary financial advisors build and maintain relationships with clients by taking the time to understand their unique financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term objectives. They work closely with clients to develop comprehensive financial plans that address various aspects of their financial lives, such as retirement planning, tax strategies, investment management, and estate planning.
Fiduciaries are legally obligated to act in the best interests of their clients at all times, ensuring that recommendations are aligned with the client's goals and objectives.
- Fiduciaries prioritize developing long-term relationships based on trust, transparency, and open communication.
- They provide ongoing support and guidance to help clients navigate life changes and financial challenges.
- Fiduciaries often offer a high level of personalized service, taking the time to educate clients and involve them in the decision-making process.
- Client meetings focus on comprehensive financial planning and goal setting, rather than just executing transactions.
Brokers
Brokers, on the other hand, typically have a more transactional approach to client relationships. They may focus on buying and selling securities or other financial products without necessarily considering the broader financial needs and goals of their clients. Brokers are generally held to a suitability standard, which means that recommendations must be suitable based on a client's financial situation and investment objectives, but not necessarily in their best interests.
- Broker-client relationships may be more focused on individual transactions and investment products rather than holistic financial planning.
- Brokers may have less frequent contact with clients and may not provide the same level of ongoing support and guidance as fiduciaries.
- Client meetings with brokers may be more transaction-oriented, with a focus on buying or selling specific investments.
- Brokers may receive commissions or other forms of compensation based on the products they sell, which can create potential conflicts of interest.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the differences between fiduciary financial advisors and brokers are vast and impactful, shaping the way they interact with clients and provide financial guidance. By understanding these disparities, individuals can make informed decisions about who to trust with their financial well-being.
FAQ Summary
What legal standards do fiduciary financial advisors follow?
Fiduciary financial advisors are held to a fiduciary duty to act in the best interest of their clients at all times.
How are fiduciary financial advisors compensated?
Fiduciary financial advisors are typically compensated through a fee-based model, aligning their interests with those of their clients.
What distinguishes the client relationships of fiduciary financial advisors from brokers?
Fiduciary financial advisors focus on building personalized, long-term relationships with clients, unlike the transactional approach often seen with brokers.